Cornelius Eanes's Programming Portal
Assignments (Nested Loops)
[111] Nesting Loops
Goal: Learn what a nesting loop is and how to use it.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: PROGRAM_NAME
/// File Name: NestingLoops.java
/// Date Finished: Feb 29, 2016
public class NestingLoops
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
// this is #1 - I'll call it "CN"
for ( char n='A'; n <= 'E'; n++ )
{
for ( int c=1; c <= 3; c++ )
{
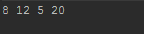
System.out.println( c + " " + n );
// The variable controlled by the inner loop (n) changes faster.
// By switching the order of the variables, the number displays first,
// rather than the letter.
}
}
System.out.println("\n");
// this is #2 - I'll call it "AB"
for ( int a=1; a <= 3; a++ )
{
for ( int b=1; b <= 3; b++ )
{
System.out.print( a + "-" + b + " " );
// By changing the 'print' statement to a 'println' statement, the
// pairs of numbers are printed on separate lines.
}
System.out.println();
// By putting a println() call here, a 3x3 grid of ordered numbers now forms.
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
}
Output
[112] Odometer Loops
Goal: Learn how braces can affect loops.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Odometer Loops
/// File Name: OdometerLoops.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
import java.util.Scanner;
public class OdometerLoops
{
public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
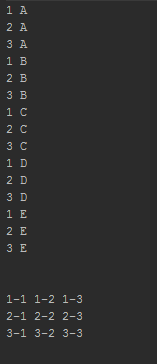
System.out.println("Input a base to count in.");
System.out.print("> ");
int base = input.nextInt();
for ( int thous=0; thous<base; thous++ )
for ( int hund=0; hund<base; hund++ )
for ( int tens=0; tens<base; tens++ )
for ( int ones=0; ones<base; ones++ )
{
System.out.print( " " + thous + "" + hund + "" + tens + "" + ones + "\r" );
Thread.sleep(10);
}
System.out.println();
}
// Removing the braces from the first 3 loops doesn't affect the output.
}
Output
[113] Basic Nested Loops
Goal: Create a basic nested loop.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Basic Nested Loops
/// File Name: BasicNestedLoops.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
public class BasicNestedLoops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
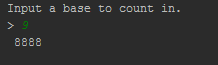
for (int x = 0; x <= 5; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y <= 5; y++) {
System.out.print("(" + x + "," + y + ") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output
[114] Multiplication Table
Goal: Create a multiplication table.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Multiplication Table
/// File Name: MultiplicationTable.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
public class MultiplicationTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("x | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12");
System.out.println("---+-----------------------------------------------------");
for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%2s", i) + " |");
for (int j = 1; j <= 12; j++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%4s", i * j));
}
System.out.println();
}
// The String.format(String, Object...) methods are just to make the output
// look prettier.
}
}
Output

[115] Number Puzzle I
Goal: List 2-digit numbers whose sum is 60 and difference is 14.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Number Puzzles 1
/// File Name: NumberPuzzle1.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
public class NumberPuzzle1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {
if (i + j == 60 && i - j == 14) {
System.out.println("(" + i + "," + j + ")");
}
}
}
}
}
Output

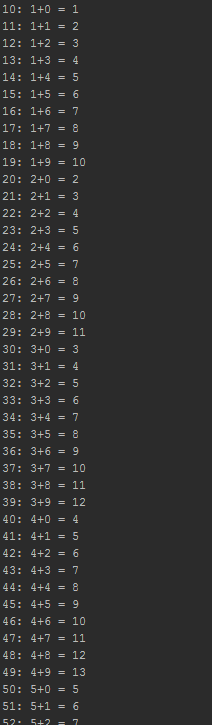
[116] Getting Individual Digits
Goal: Generate a list of all positive 2-digit numbers.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Getting Individual Digits
/// File Name: IndividualDigits.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
public class IndividualDigits {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i + "" + j + ": " + i + "+" + j + " = " + (i + j));
}
}
}
}
Output
[117] More Number Puzzles
Goal: Give the user a choice between generating two different number lists.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: More Number Puzzles
/// File Name: NumberPuzzle2.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberPuzzle2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = -1;
while (choice != 3) {
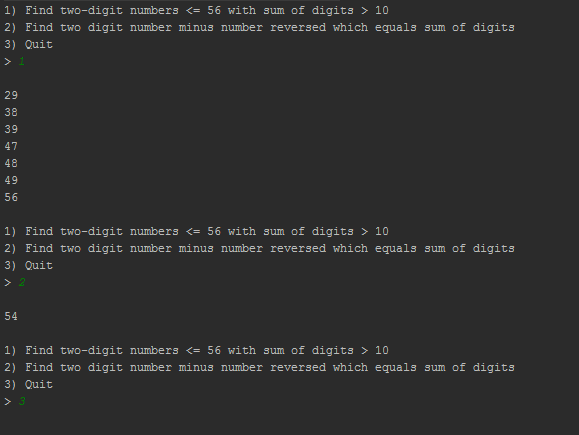
System.out.println("1) Find two-digit numbers <= 56 with sum of digits > 10");
System.out.println("2) Find two digit number minus number reversed which equals sum of digits");
System.out.println("3) Quit");
System.out.print("> ");
choice = input.nextInt();
System.out.println();
if (choice == 1) {
func1();
} else if (choice == 2) {
func2();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void func1() {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int n = i * 10 + j;
if (n <= 56 && i + j > 10) {
System.out.println(n);
}
}
}
}
public static void func2() {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int n1 = i * 10 + j;
int n2 = j * 10 + i;
if (n1 - n2 == i + j) {
System.out.println(n1);
}
}
}
}
}
Output
[118] Number Puzzles III: Armstrong Puzzles
Goal: Generate a list of all 3-digit Armstrong numbers.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Number Puzzles III: Armstrong Numbers
/// File Name: NumberPuzzles3.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
public class NumberPuzzles3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 1; x < 10; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < 10; y++) {
for (int z = 0; z < 10; z++) {
int n = x * 100 + y * 10 + z;
int c1 = x * x * x;
int c2 = y * y * y;
int c3 = z * z * z;
if (n == c1 + c2 + c3) {
System.out.println(n);
}
}
}
}
}
}
Output

[119] Number Puzzles IV: A New Hope
Goal: Explained here.
/// Name: Cornelius Eanes
/// Period: 5
/// Program Name: Number Puzzles IV: A New Hope
/// File Name: NumberPuzzles4.java
/// Date Finished: Mar 01, 2016
public class NumberPuzzles4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int a = 0; a < 1000; a++) {
for (int b = 0; b < 1000; b++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 1000; c++) {
for (int d = 0; d < 1000; d++) {
int m = a + 2;
boolean c1 = b - 2 == m && c * 2 == m && d / 2 == m;
boolean c2 = a + b + c + d == 45;
if (c1 && c2) {
System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + c + " " + d);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Output